Managing a lab involves numerous tasks, from tracking experiments to ensuring equipment availability. To streamline these responsibilities, Uncountable has introduced the Notebook Dashboard, a feature within the Integrated Electronic Laboratory Notebook (ELN) tool. The Notebook Dashboard provides a real-time view of key lab activities, combining critical data, visualizations, and analytics.
Designed for both frequent users and those who interact less often, like managers and executives, the Notebook Dashboard pulls platform data into live charts and tables, updating as your team works. Whether you’re hands-on in the lab or need a high-level overview, the Notebook Dashboard provides insights to optimize decision-making and resource management.
Notebook Dashboard Use Cases
Use the Notebook Dashboard to visualize real-time data effectively with live-updating bar charts, pie charts, line charts, and radar charts. This flexibility is particularly useful for monitoring experiment-related metrics, managing lab utilization, and tracking project progress:
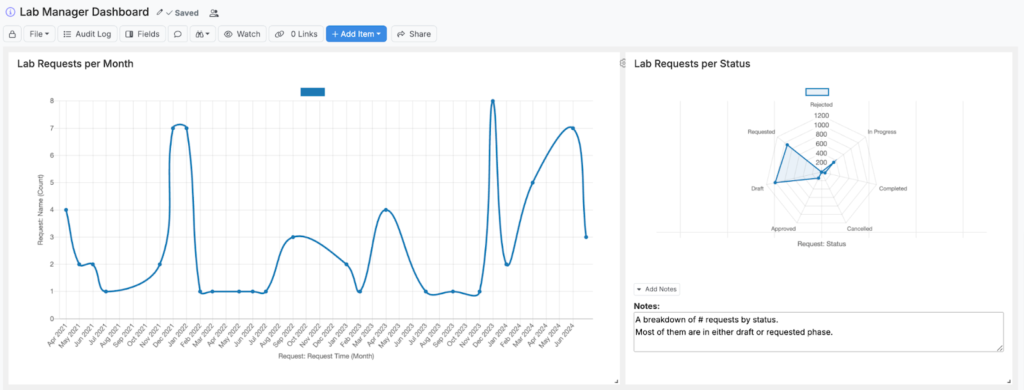
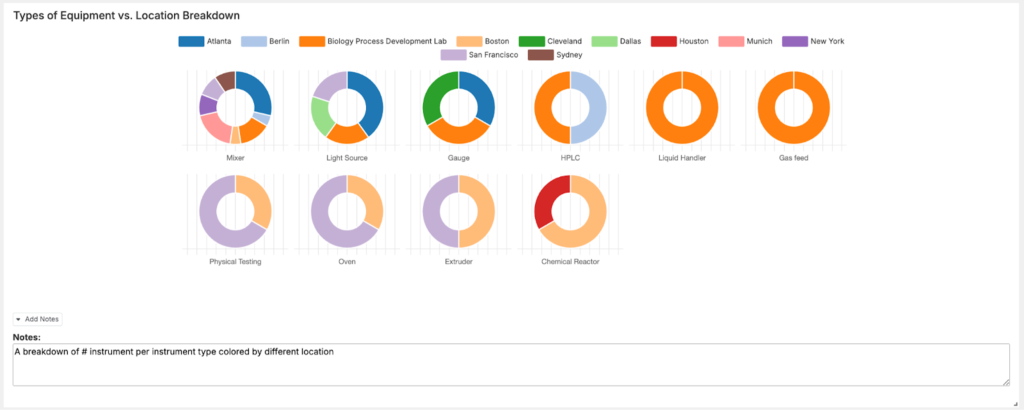
- Lab Utilization Reporting: Use a line or radar chart to track resource allocation across labs, equipment, and personnel.
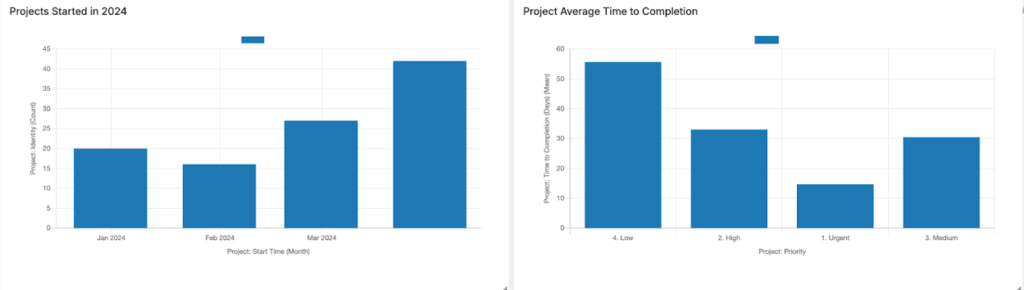
- Project Tracking: Report key project metrics like project duration, cost, and success rate, allowing lab managers to stay on top of critical project timelines and objectives.
- Statistical Process Control (SPC) Charting: Proactive monitoring of product performance with SPC charts and real time “out-of-spec” notifications.
Creating a Notebook Dashboard
- Create a Notebook: Navigate to the Notebooks page, click the blue “Add” button, and select “Notebook”.
- Name the Notebook and check the “Dashboard Type” checkbox to ensure you’re setting up a Dashboard rather than a standard ELN. Then, click “Add Notebook”.
- Add a chart: Begin adding to your Notebook Dashboard by clicking the blue “Add Item” button. To add a chart, first select “Chart” from the dropdown menu. From here, you can also add text, custom tables, embedded websites, structured listings, etc.
- Configure your chart: Add data to your chart by clicking “Edit Chart Configuration”.
- Select data sources: From the Configure Chart modal, you will select relevant data sources, such as experiments or equipment. First, select your base data source from the dropdown menu. This will populate the listing.
In the example below, we will create a “Experiments per Scientist” bar chart by first selecting “Experiment” as the base.
- Group the data: Next, group your data by editing the listing columns. Click “List” and select “Set Columns”.
- Select grouping columns: Determine a new grouping column, columns by which you will group your base data source, by selecting from the dropdown menu. Delete unwanted grouping columns, by clicking on the cog and selecting “Remove Column”.
In the example below, we will group experiments by experiment creator, so we will select “Experiment Creator” as our grouping column.
- Select “Group by” from the dropdown menu beneath grouping columns, and click “Add”.
- Select aggregate columns: Aggregate column performs an operation (sum, average, count, etc.) on grouped data. First, select an aggregate column by choosing from the dropdown menu.
In the example below, we are grouping experiments by experiment creator, so we will select “Experiment” + “Identity” from the dropdown menu.
- Select an operation from the dropdown menu before clicking “Add”. By default, the aggregate column will typically be a count.
- Save your columns. This will return you to the Configure Chart page.
- Select your chart type: Next, select your chart type (bar, line, pine, or radar).
- Set chart axes and groupings: Determine how the data will be plotted by selecting from the dropdown menus. This will generate a preview of your graph above. Selections are dependent on chart type:
- Bar Chart:
- Height: The vertical value of each bar, measuring the magnitude of data points.
- X-axis: The horizontal axis, used to categorize or label the data points.
- Grouping (optional): Enables comparison within categories by grouping multiple bars together.
- Line chart:
- Y-axis: The vertical axis, measuring magnitude of data points.
- X-axis: The horizontal axis, used to categorize or label the data points.
- Line (optional): The continuous line which shows trends over the X-axis.
- Pie Chart:
- Chart Area: The whole dataset to be plotted.
- Pie Slices: The individual sections, representing a portion of the whole dataset.
- Division: How the data is divided, based on percentages or parts of the whole.
- Radar Chart:
- Radius: Distance from the center to edge, measuring the magnitude of data points.
- Axes: Lines radiating from the center, representing different variables of the data.
- Rings (optional): Concentric circles that serve as a reference grid.
- Bar Chart:
In the example below, we will use a bar chart and plot the Experiment count on the Y-axis (height) against Experiment Creator on the X-axis.
- Save your chart: Once you have made all necessary selections, click “Save” to add the chart to your Notebook Dashboard.
Customizing Your Notebook Dashboard
Once your charts have been added, you can further customize your Notebook Dashboard by resizing charts, changing their titles, adding notes, or deleting items that are no longer relevant.
To resize your chart, click and drag the arrow in the bottom right corner.
To configure, edit, move, or delete your chart, click the cog icon in the top right corner to access.
Adding Filters to Your Notebook Dashboard
Filters can be applied to notebook dashboards to refine the data displayed. You can add filters for both categorical and numeric data types. To create a filter control cell, click “Add Item” and select “Filter Control”.

Then, select the entity type you want to filter.


Adding Interactive Pill/Slider Filters
Users can also add interactive pill/slider filters to categorical or numeric data on the Notebook Dashboard.
Pill Filters
To create categorical pill filter, select one or more values using the “includes” option. A gray plus sign will appear, which you can click to further configure the filter.

From this modal, first add a Filter name (Object 1). Then, select options to display within the filter (Object 2). Leaving this blank will add all available options to the pill filter upon creation. When ready, click “Accept”.


Slider Filter
To create a numeric slider filter, set a range using the “within” option and click the gray plus sign.

Name your filter and specify a range for the slider. Then, click “Accept”.


